

Billiard Path Destinations:Let {$m,n\in\mathbb N$} be the dimensions of a rectangle.
Proof: First, note that the final destination of the path on the {$x\times y$} rectangle is the same as the destination on the {$kx\times ky$} rectangle. It's the shape of the rectangle, not the size, that determines corner destination. Thus, for option 1., we can assume that {$m$} is even and {$n$} is odd. Now color the intersections of the rectangle alternately, red and blue. 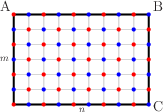 The path always runs over red intersections, never blue intersections. 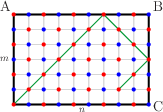 Thus, the path must end at corner A, the only red corner. Similarly, for option 2., C is the only red corner. And for option 3., we can assume that both {$m$} and {$n$} are odd, and the only red corner is B. |